Private Subdomain Takeover: Missing Origin Elastic Beanstalk Instance
Risk Level: Medium
Description:
This plugin detects Route53 records from private hosted zones pointing to the Elastic Beanstalk instance where the corresponding application is not present. Such configuration can lead to a domain takeover where a malicious user can create an instance with the same DNS name in another AWS account and upload content. The attacker can then change the taken-over domain to look like an internal employee portal and make employees submit confidential information.
About the Service :
Amazon Route 53 is a cloud Domain Name System (DNS) web service that is highly accessible and scalable. It is intended to provide developers and businesses with a highly dependable and cost-effective method of routing end users to Internet applications.
Amazon Route 53 connects user requests to AWS infrastructure such as Amazon EC2 instances, Elastic Load Balancing load balancers, and Amazon S3 buckets, as well as equipment outside of AWS.
Impact:
A domain takeover can occur if a malicious user creates an instance with the same DNS name in another AWS account and uploads content.
The attacker can then disguise the hijacked domain as an internal employee site and force employees to submit sensitive information.
Steps to reproduce :
- Login to AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to Route 53 dashboard. (https://console.aws.amazon.com/route53/ )

- Next, move to the “Hosted Zone” in the left navigation panel under Route 53.
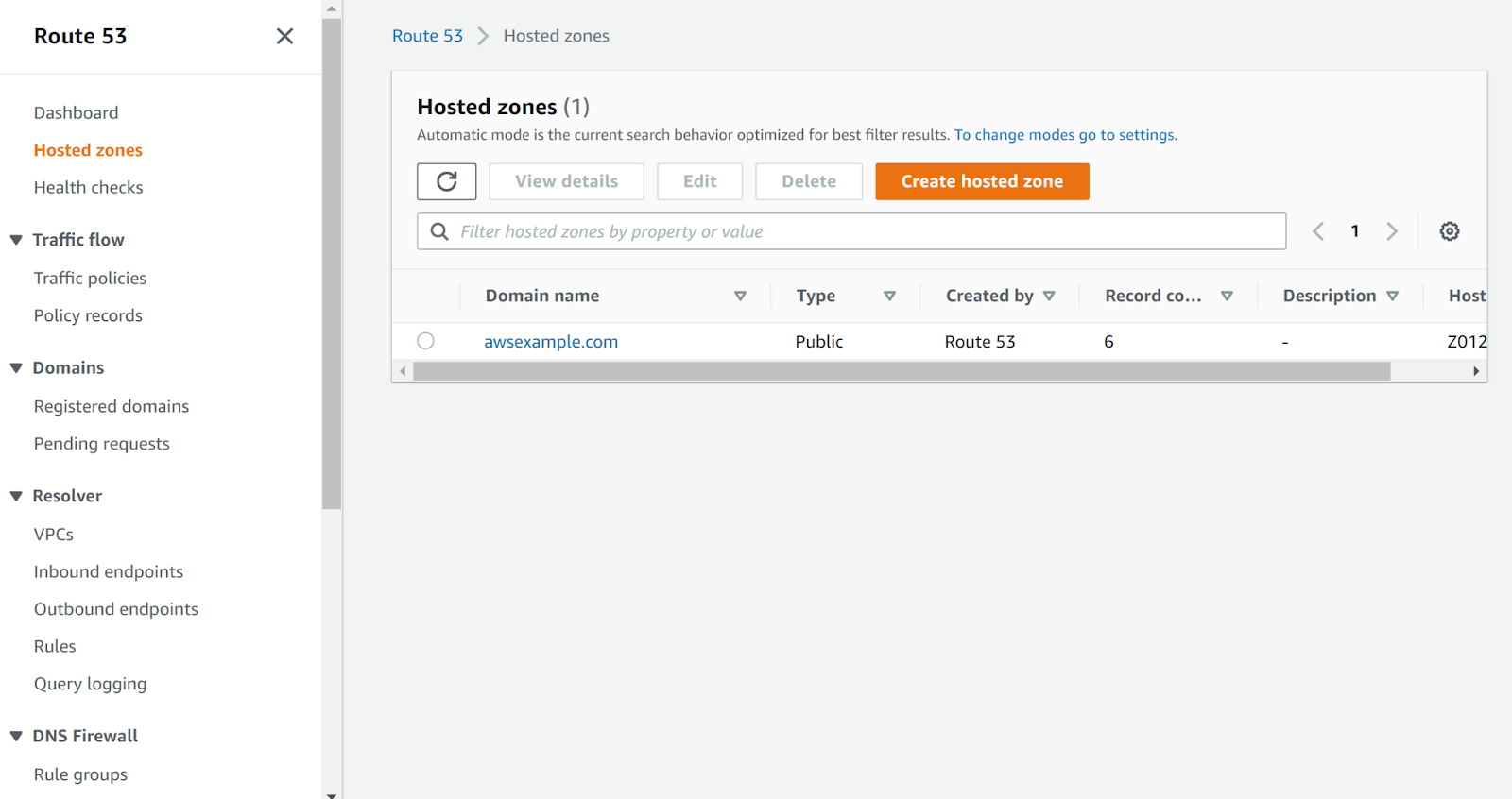
- Select the hosted zone to examine.
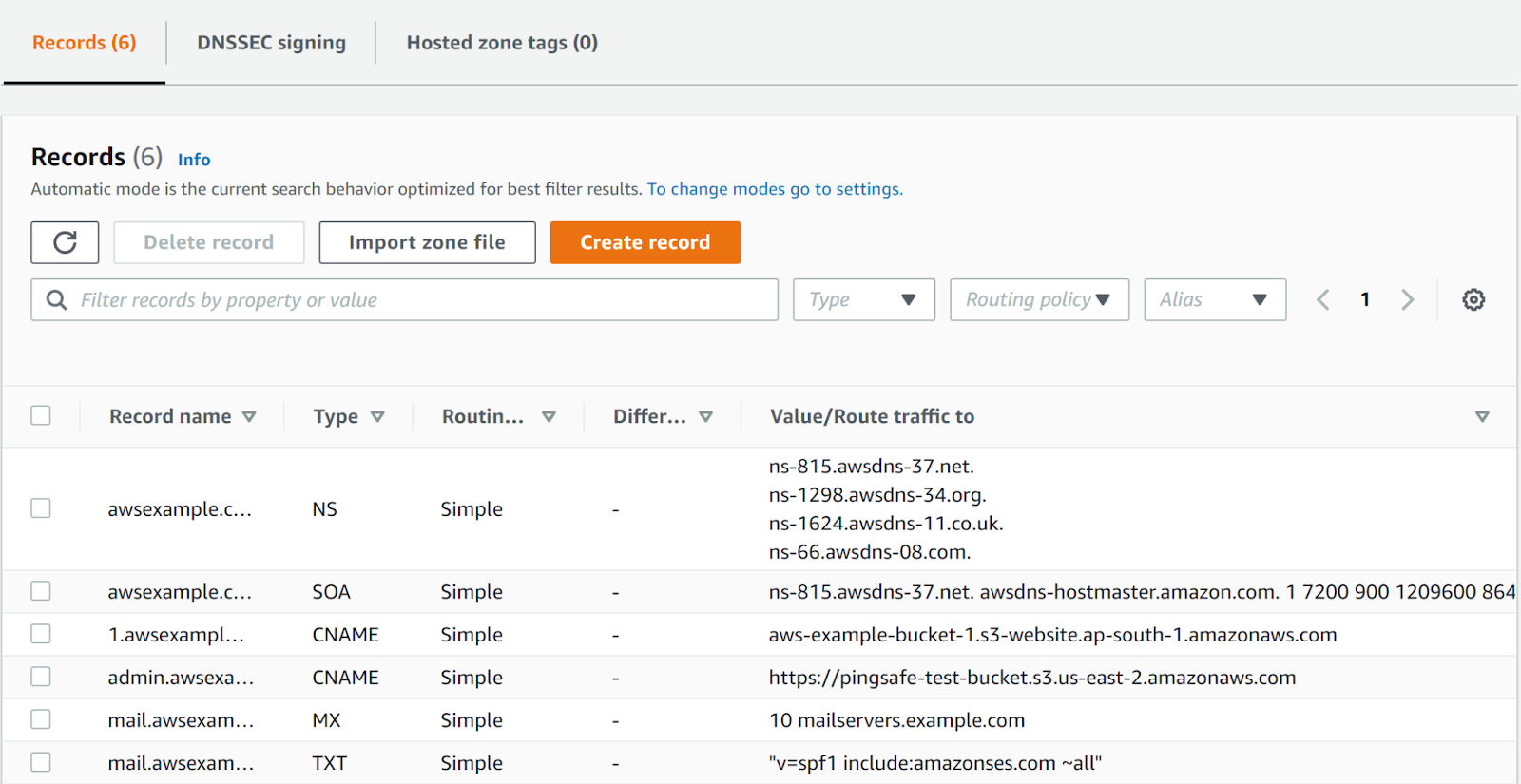
- Expand the Hosted Zone details. Proceed for the next steps if the Type is set to “Private hosted zone”.
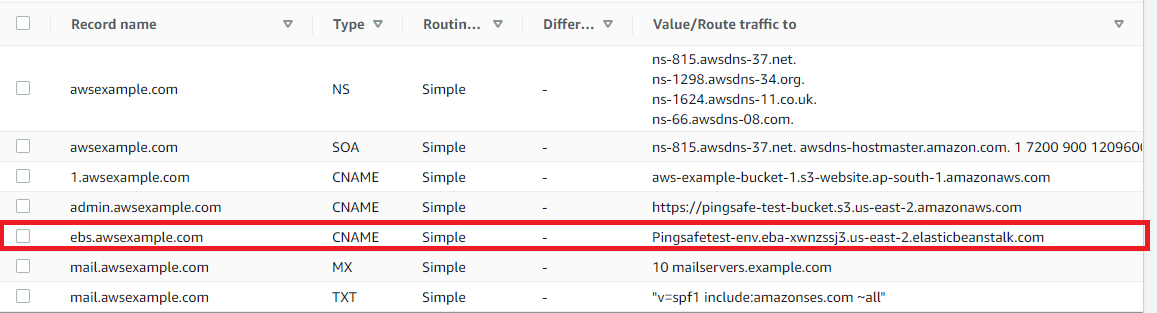
- Next, check the record which has the elastic beanstalk, and look at the instance where it is routing its value.
- Copy the name of the elastic beanstalk.
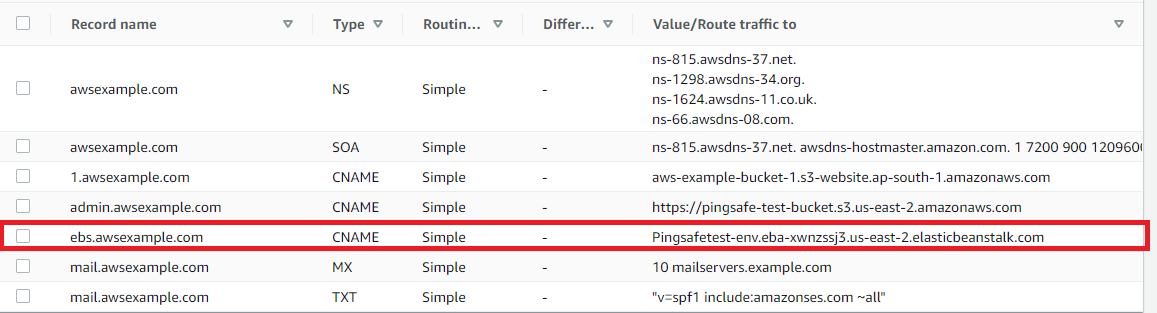
- Navigate to the Elastic Beanstalk dashboard at: https://console.aws.amazon.com/route53/
- Search for the name of the copied Elastic beanstalk instance.
- If there is no result for it, the instance is missing and hence it is vulnerable to takeover.
Steps for remediation :
Ensure that all such Route53 records are removed.
- Login to AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to Route 53 dashboard. (https://console.aws.amazon.com/route53/ )

- Next, move to the “Hosted Zone” in the left navigation panel under Route 53.
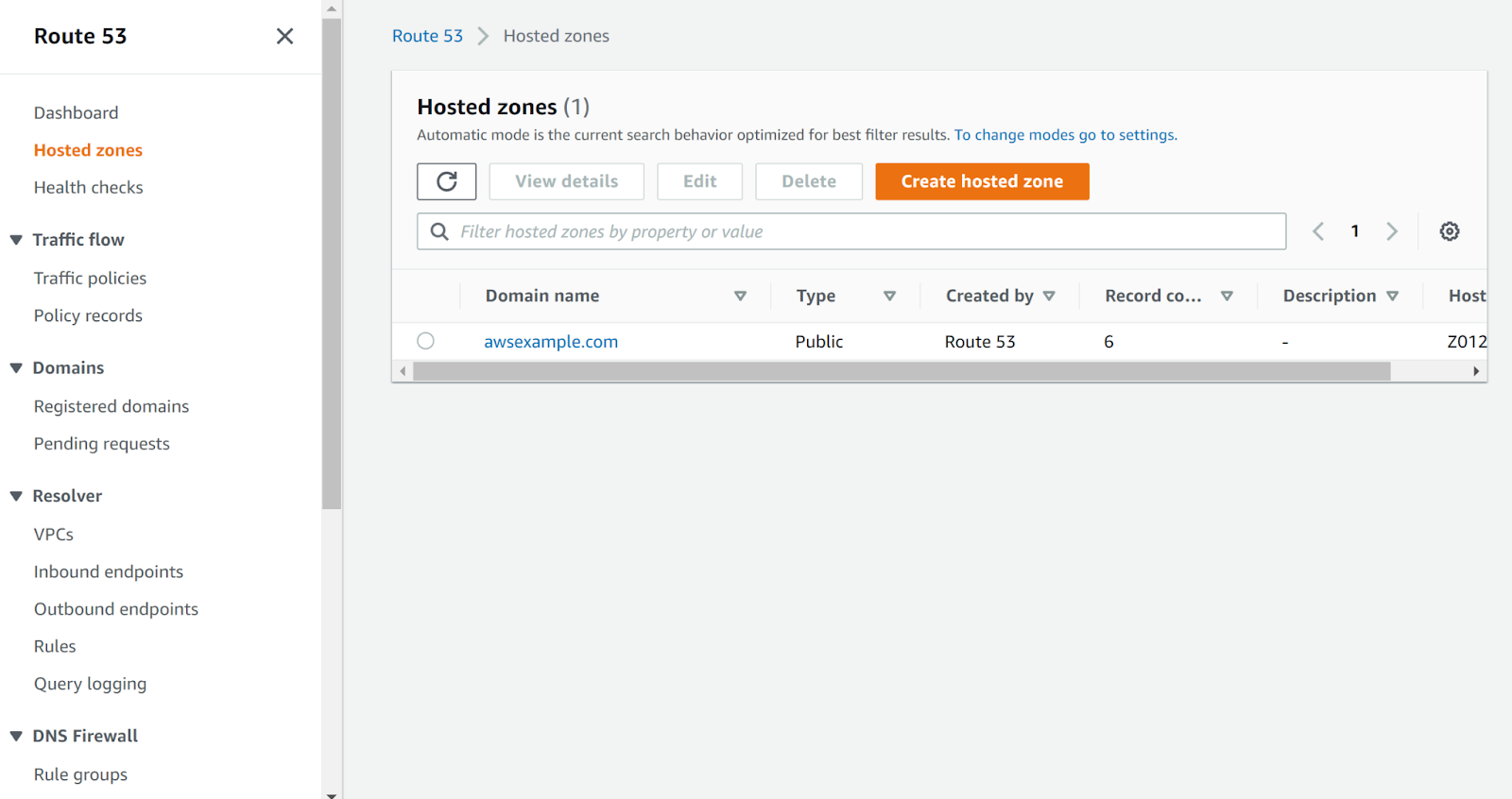
- Select the hosted zone to examine.
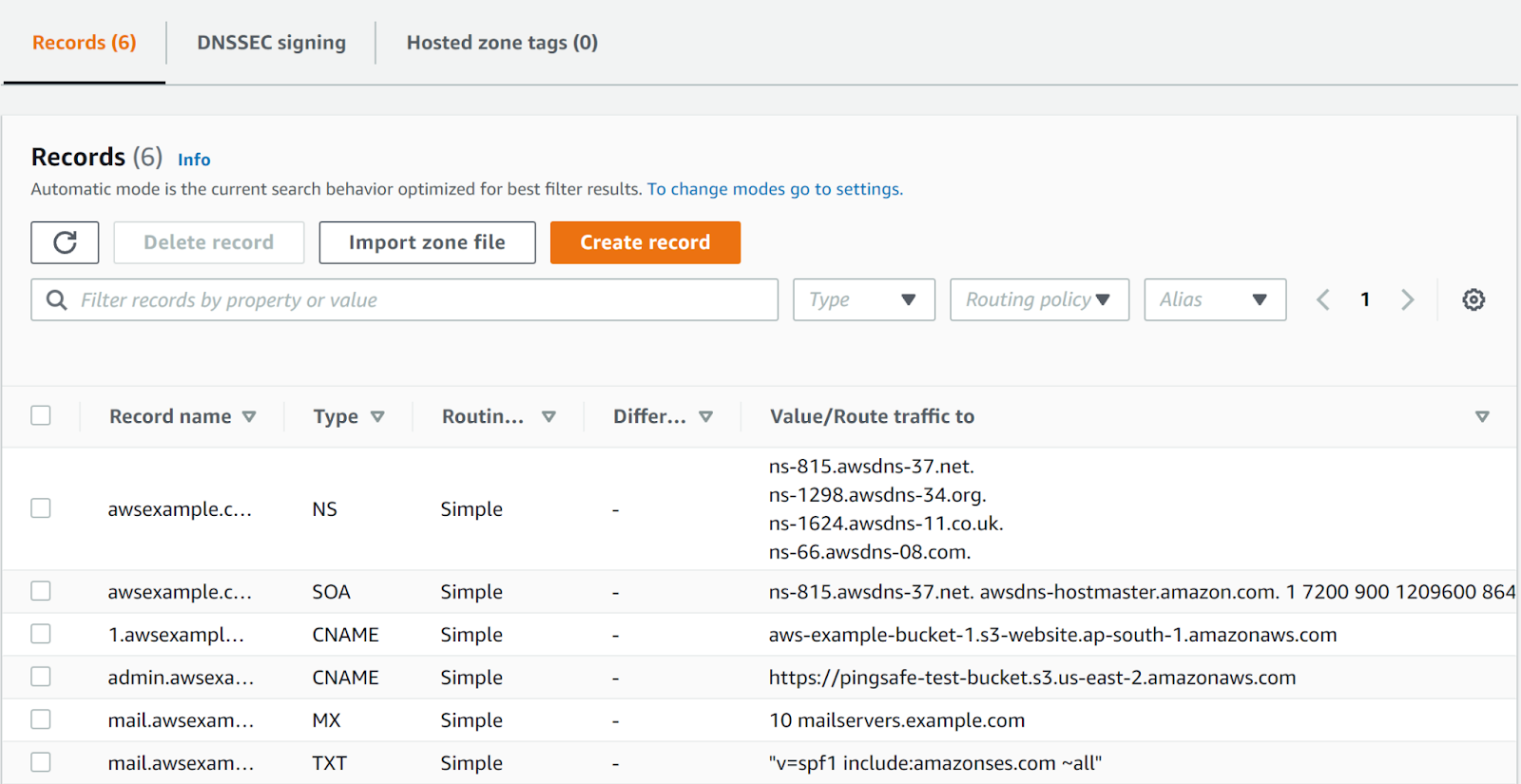
- Next, check the record which has the elastic beanstalk, and look at the instance where it is routing its value.
- Copy the name of the elastic beanstalk.
- Navigate to the Elastic Beanstalk dashboard at: https://console.aws.amazon.com/route53/
- Search for the name of the copied Elastic beanstalk instance.
- If there is no result for it, the instance is missing and hence it is vulnerable to takeover.
- Move back to the Route 53 dashboard and inside hosted zones, delete the record of the elastic beanstalk.